Running Head: MicroRNA-144 and Airway Immune Dysfunction in COPD
Funding Support: This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation for Young Scientists of Shanxi Province, China (No.20210302124179).
Date of Acceptance: April 22, 2025 | Published Online: April 25, 2025
Abbreviations: 16HBECs=human bronchial epithelial cells; AECOPD=acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; ALI=air-liquid interface; cDNA=complementary DNA; CON=control; COPD=chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CSE=cigarette smoke extract; GAPDH=glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GOLD=Global initiative for chronic Obstructive Lung Disease; IgA=immunoglobin A; LR=lower right; MEM=Minimum Essential Medium; miR-144=microRNA-144; miRNAs=microRNAs; OD=optical density; PBS=phosphate-buffered saline; pIgR=polymeric immunoglobulin receptor; qRT-PCR=quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; sIgA=immunoglobulin A; TGF-β=transforming growth factor beta; TGIF-1=transforming growth factor beta-induced factor homeobox 1; UR=upper right
Citation: Liu H, Zhao Y, Cao J, Liang L, Zhou J. The role of microRNA-144 in regulating airway immune dysfunction in COPD through the transforming growth factor-beta/polymeric immunoglobulin receptor pathway: an in vitro study. Chronic Obstr Pulm Dis. 2025; 12(4): 285-293. doi: http://doi.org/10.15326/jcopdf.2024.0592
Introduction
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death worldwide, posing a significant public health challenge.1 COPD is marked by persistent airflow limitation, often resulting from prolonged exposure to harmful particles or gases that damage airway and alveolar structures. A key feature of COPD is the occurrence of acute exacerbations (AECOPDs), which are sudden episodes of worsening symptoms. Repeated AECOPD events accelerate lung function decline, diminish quality of life, and raise mortality risks, while also contributing to substantial health care costs.2 Research indicates that respiratory tract infections account for 60%–80% of these exacerbations, highlighting the importance of airway immune dysfunction in the susceptibility to infection.3 Understanding the mechanisms that contribute to immune dysfunction in the airways of COPD patients is essential for developing targeted therapeutic strategies.
Secretory immunoglobulin A (sIgA) is an essential component of the humoral immune response, working in tandem with the mucociliary barrier to defend against pathogens, including bacteria, through mechanisms such as agglutination, neutralization, and mucosal immune responses that activate host complement pathways to protect the airways and lung tissues.4 The 2018 Global initiative for chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) guidelines were the first to highlight airway mucosal immune dysfunction in COPD, noting a close link between sIgA deficiency and pathological features of COPD, including small airway inflammation and remodeling.5 sIgA plays a vital role in airway immunity and COPD pathology, yet it is critical to distinguish between its 2 forms: monomeric serotype IgA and the dimeric, secretory form.5 The latter, produced by lung plasma cells, binds to the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR) at the base of airway epithelial cells for transport to the bronchial and alveolar spaces, where it becomes sIgA with active mucosal immune functions.6 Thus, pIgR is essential for airway mucosal immunity and is implicated in COPD pathogenesis, positioning it as a potential therapeutic target for addressing AECOPDs and restoring mucosal immunity. Studies show that as airway remodeling advances, pIgR expression declines, leading to lower sIgA levels on the airway mucosa.7,8 Animal research suggests that diminished pIgR expression heightens infection susceptibility and may contribute to emphysema development.9,10 Additionally, proteomic analyses reveal decreased pIgR in COPD patients who experience frequent acute exacerbations, highlighting pIgR as a crucial factor in airway mucosal immunity and COPD progression.11 During the process, one emerging mechanism involves the transforming growth factor‑beta (TGF‑β) pathway. TGF-β is a key immunoregulatory cytokine involved in maintaining epithelial homeostasis and immune tolerance. The TGF-β-pIgR pathway plays a crucial role in mucosal immunity and inflammation regulation, particularly in epithelial barriers such as the respiratory and intestinal tracts.12 TGF-β signaling upregulates the expression of pIgR, which is essential for the transcytosis of polymeric immunoglobulin A (IgA), thereby enhancing mucosal immune defense. In COPD, dysregulation of TGF-β signaling may lead to reduced pIgR expression, impairing IgA-mediated immune protection and increasing susceptibility to infections and inflammation.13
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, noncoding RNAs, 21–25 nucleotides in length, that regulate gene expression by targeting messenger RNAs for degradation or inhibiting translation.14 They participate in various biological processes, including inflammation, cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and immune responses.14 Recent studies indicate that miRNAs are critically involved in COPD pathogenesis.15 For instance, microRNA-144 (miR-144) expression is notably upregulated in the lung tissues of COPD patients compared to healthy smokers.16 Research using miR-144 knockout mice demonstrates heightened immune responses against influenza virus replication, suggesting that elevated miR-144 in COPD patients may contribute to diminished airway immune function.17 This immune dysfunction creates a unique lung microenvironment in COPD patients, marked by increased colonization of pathogenic bacteria, such as Haemophilus, Streptococcus, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, and Moraxella, which drives chronic inflammation and accelerates disease progression.18 Despite these insights, the specific mechanisms by which miR-144 influences immune regulation in COPD remain to be fully elucidated.
To address this knowledge gap, our study aims to investigate whether miR-144 contributes to COPD pathogenesis and progression by modulating pIgR expression and impacting sIgA levels. Since TGF-β downregulates pIgR in mucosal epithelial cells, reducing sIgA transport to the mucosal surface, we will also examine TGF-β’s role within the miR-144/pIgR regulatory pathway.13 Additionally, TGIF-1, a negative feedback regulator in the TGF-β pathway, may indirectly impact TGF-β’s regulation of pIgR and warrants further investigation.19 Elucidating these interactions could reveal key molecular mechanisms driving COPD progression.
In summary, we propose that miR-144 is a central regulator of COPD development and progression by modulating pIgR expression through TGF-β, thus affecting airway sIgA levels. Transforming growth factor beta-induced factor homeobox 1 (TGIF-1) may also play a significant role in this regulatory pathway. To test this hypothesis, we used a human bronchial epithelial cell (16HBEC) model to examine the effects of cigarette smoke extract (CSE) on the expression of miR-144, TGIF-1, TGF-β, and pIgR. We further assessed changes in TGIF-1, TGF-β, and pIgR levels following miR-144 inhibition or overexpression to clarify miR-144’s role in this pathway. Finally, we explored TGF-β’s regulatory function by analyzing molecular changes with TGF-β inhibition.
Methods
Cell Culture
16HBECs were obtained from ScienCell Research Laboratories, Inc., (Carlsbad, California) and cultured in Minimum Essential Medium (MEM) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.; Waltham, Massachusetts) with 10% fetal bovine serum (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.; Waltham, Massachusetts). The cells were maintained at 37°C in a humidified incubator with 5% CO₂ and saturated humidity.
To establish an air-liquid interface (ALI) for differentiation, the 16HBECs were first cultured under submerged conditions in complete growth medium for 3–4 days to allow for cell attachment and proliferation. Once the cells reached approximately 70% confluence, the culture medium was switched to a differentiation medium, and the cells were exposed to air at the apical surface while maintaining the basal medium. The ALI culture was maintained for 7–10 days to promote differentiation into ciliated columnar epithelial cells, with the basal medium replaced every 2–3 days. Evidence of mucociliary differentiation was confirmed by the presence of ciliary formation observed in the ALI cultures.
Preparation of Cigarette Smoke Extract (CSE)
CSE was prepared based on a modified version of the method as described previously.20 A Da Qian Men cigarette (0.013g tar, 0.001g nicotine, 0.014g CO) (Taiyuan Tobacco Company; Taiyuan, China) was connected to a syringe containing 20ml of serum-free MEM to replicate human smoking conditions. The cigarette was lit, and smoke was drawn into the syringe for 2 seconds, followed by a 58-second pause for absorption. This process took about 7–8 minutes per cigarette, with 2 cigarettes processed consecutively for each preparation. The resulting 20ml of serum-free MEM was adjusted to a pH of 6.8–7.2 using 1N NaOH (Amresco, Inc.; Farmingham, Massachusetts) and filtered through a 0.22µm membrane (Merck Millipore; Shanghai, China) for sterilization. The CSE stock was then diluted with serum-free MEM to create working concentrations of 0% (control [CON], no CSE), 1%, 2%, 5%, and 10% for experimental use. To maintain consistency, all CSE preparations were used within 30 minutes of preparation.
Cell Counting Kit-8 Assay
The proliferation of 16HBECs was assessed using the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) (KGA317, Jiangsu KGI Biotechnology Co., Ltd.; Jiangsu Province, China). Cells were digested and counted to prepare a cell suspension of 1 × 10⁵ cells/mL. Then, 100μL of the suspension was seeded into each well of a 96-well culture plate and incubated at 37°C in a 5% CO₂ incubator for 24 hours. The drug was diluted to the desired concentrations with conditioned medium, and 100μL of the drug-containing medium was added to each well to establish the experimental and negative control groups. After 24 hours of incubation, 10μL of CCK-8 solution was added to each well, and the plate was incubated for an additional 2 hours. The mixture was then gently agitated for 10 minutes to ensure even distribution. The optical density (OD) at 450nm was measured using a microplate reader to determine the cell proliferation inhibition rate, calculated as follows: inhibition rate (%) = ((OD_control - OD_treatment) / OD_control) × 100%.
Annexin V-APC/7-AAD Staining
Apoptosis in 16HBECs was detected using Annexin V-APC/7-AAD double staining (Annexin V-APC/7-AAD Apoptosis Detection Kit, KGA1024, Jiangsu KGI Biotechnology Co., Ltd.; Jiangsu Province, China). Cells were washed twice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) by centrifuging at 1000rpm for 5 minutes, and 5 × 10⁵ cells were collected. The cells were then resuspended in 500μL of Binding Buffer. Next, 5μL of Annexin V-APC was added to the suspension, mixed gently, followed by the addition of 5μL of 7-AAD, with gentle mixing after each addition. The samples were incubated in the dark at room temperature for 5–15 minutes. Apoptosis was measured using a flow cytometer (Becton-Dickinson FACS Calibur, BD; Franklin Lakes, New Jersey), with data analysis focusing on the distribution of cells across 4 quadrants: viable cells (lower left), early apoptotic cells (lower right [LR]), late apoptotic cells (upper right [UR]), and necrotic cells (upper left).The apoptosis rate (%) was calculated by summing the percentages of early and late apoptotic cells, as follows: Apoptosis (%) = UR (%) + LR (%).
Cell Transfection
To examine the role of miR-144 in modulating TGIF-1, TGF-β, and pIgR expression under CSE stimulation, transient transfection was conducted on mature, differentiated 16HBECs. Cells were seeded in 6-well plates at 70%–80% confluence and transfected with either a miR-144 inhibitor or miR-144 mimics using Lipofectamine RNAiMAX (Thermo Fisher Scientific), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. For inhibition studies, cells were grouped as follows: control (no inhibitor), low-dose miR-144 inhibitor (50nmol/L), and high-dose miR-144 inhibitor (100nmol/L). For overexpression studies, cells were divided into control (no mimic), low-dose miR-144 mimic (50nmol/L), and high-dose miR-144 mimic (100nmol/L) groups. After 24 hours, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analysis was used to confirm the successful inhibition or overexpression of miR-144. To validate the role of TGF-β in regulating pIgR expression under miR-144 overexpression, we established 3 experimental groups: control, miR-144 overexpression, and miR-144 overexpression with TGF-β inhibition. TGF-β inhibition was achieved by treating the cells with the TGF-β receptor inhibitor SB431542 (10µM, Sigma-Aldrich) for 24 hours prior to transfection.
qRT-PCR
Total RNA was extracted from samples using TRIzol reagent, followed by chloroform and isopropanol treatments, with multiple centrifugation steps to ensure high purity. RNA concentration and purity were assessed via UV spectrophotometry. For messenger RNA quantification, purified RNA was reverse-transcribed into complementary DNA (cDNA) using the cDNA First Strand Synthesis Kit (RR036B, TaKaRa; Kyoto, Japan) with random primers. For miRNA quantification, a stem-loop real-time primer approach was used for reverse transcription of miR-144, performed with the One Step TB Green™ PrimeScript™ RT-PCR Kit II (RR086B, TaKaRa; Kyoto, Japan). To optimize reaction conditions and minimize variability, preliminary tests were conducted with diluted cDNA. Each sample was analyzed in triplicate with SYBR Green dye in a real-time PCR system (ABI StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR System, Applied Biosystems; Westminster, Colorado), using a specific thermal cycling program. Fluorescence signals were measured to quantify target gene expression.The sequences of all primers used for qRT-PCR are as follows:
miR-144-3p, Forward (5'–3'): GCGCGCGTACAGTATAGATGA, Reverse (5'–3'): AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT;
pIgR, Forward (5'–3'): GGCACCTTCACTGTCATCCTCA, Reverse (5'–3'): GAGAGTATCGCCGTTGGTCAGA;
TGF-β, Forward (5'–3'): CTATGACAAGTTCAAGCAGAGT, Reverse (5'–3'): TGAGGTATCGCCAGGAATTG;
TGIF-1, Forward (5'–3'): TGGCTCAGGCAAGAGAAGGAGA, Reverse (5'–3'): GCGGGCGTTGATGAACCAGTTA.
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), Forward (5'–3'): AGATCATCAGCAATGCCTCCT, Reverse (5'–3'): TGAGTCCTTCCACGATACCAA;
U6,Forward (5'–3'):CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA, Reverse(5'–3'):AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT
Western Blot
Adherent cells were washed twice with cold PBS (10mL per 150mm plate) to remove culture medium, shaking gently with each wash. Cells were then trypsinized at 37°C, collected, and centrifuged at 1000rpm for 10 minutes. The cell pellet was washed twice in cold PBS (1000rpm, 5 minutes each). A lysis buffer was prepared by combining 10μL phosphatase inhibitor, 1μL protease inhibitor, and 5μL of 100mM phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride with 1mL of cold lysis buffer. After washing, cells were resuspended in this buffer, incubated on a shaker at 4°C for 15 minutes, and centrifuged at 14,000rpm for 15 minutes at 4°C. The supernatant was collected as the protein extract, and protein concentration was determined using the BCA Protein Assay Kit (KGA902, Jiangsu Kaiji Biotechnology Co., Ltd.; Jiangsu Province, China). Equal amounts of protein (10µg) were separated by 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride membranes, and probed with antibodies against TGIF (ab52955, Abcam; Cambridge, United Kingdom), TGF-β (ab215715, Abcam), and pIgR (ab32536, Abcam). Bands were visualized using an electrochemiluminescence detection system, imaged with a chemiluminescent imaging system, and quantified using Gel-Pro32 software, normalized to GAPDH levels.
Results
Determining the Optimal Cigarette Smoke Extract Concentration
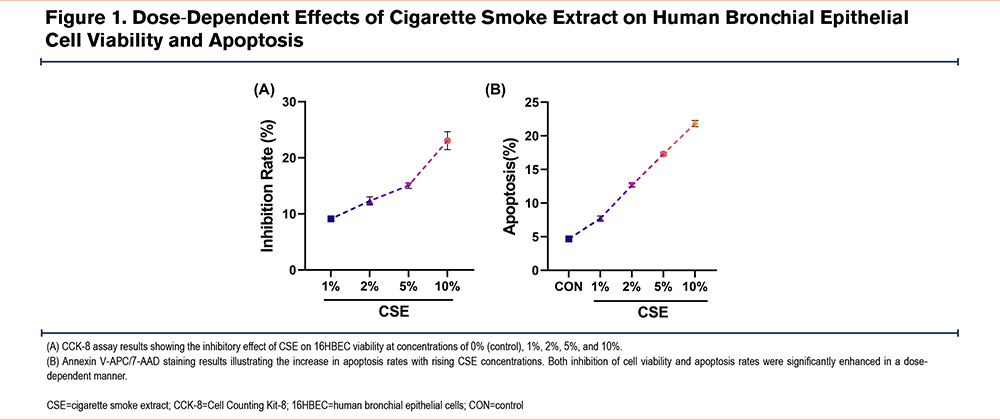
To identify the optimal concentration of CSE for our study, we prepared CSE using a modified method as described previously.20 The CSE stock solution was diluted with serum-free MEM to create working concentrations of 0% (CON), 1%, 2%, 5%, and 10%, which were then applied to 16HBECs. Cell viability and apoptosis were assessed across these concentrations using the CCK-8 assay and Annexin V-APC/7-AAD staining. Results indicated a clear dose-dependent effect of CSE on 16HBECs: as CSE concentration increased, both cell inhibition and apoptosis rates rose significantly (Figure 1A-B). Based on these findings, 10% CSE, which showed the most pronounced effects, was selected for subsequent experiments.
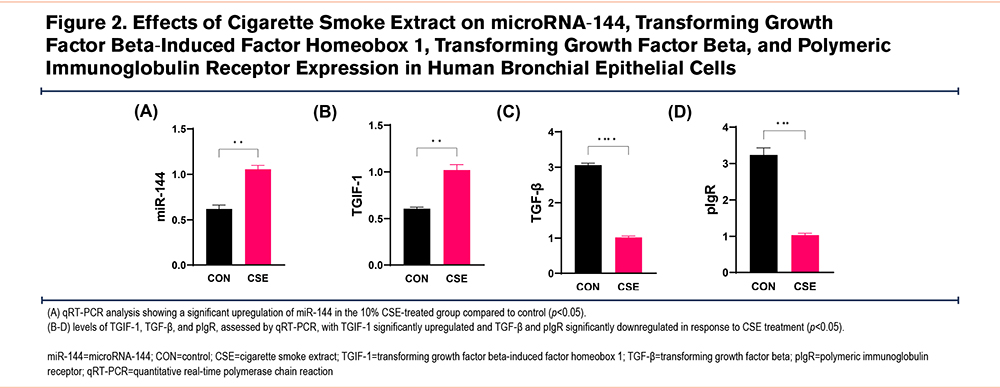
Cigarette Smoke Extract Alters Expression of miR-144, TGIF-1, TGF-β and pIgR in 16HBECs
To examine how CSE affects miR-144 expression and its regulatory mechanisms, we cultured 16HBECs and divided them into 2 groups: a control group and a group treated with 10% CSE. Post-treatment analysis using qRT-PCR revealed that CSE exposure significantly increased the expression of miR-144 and TGIF-1, while reducing TGF-β and pIgR levels compared to the control group (Figure 2).
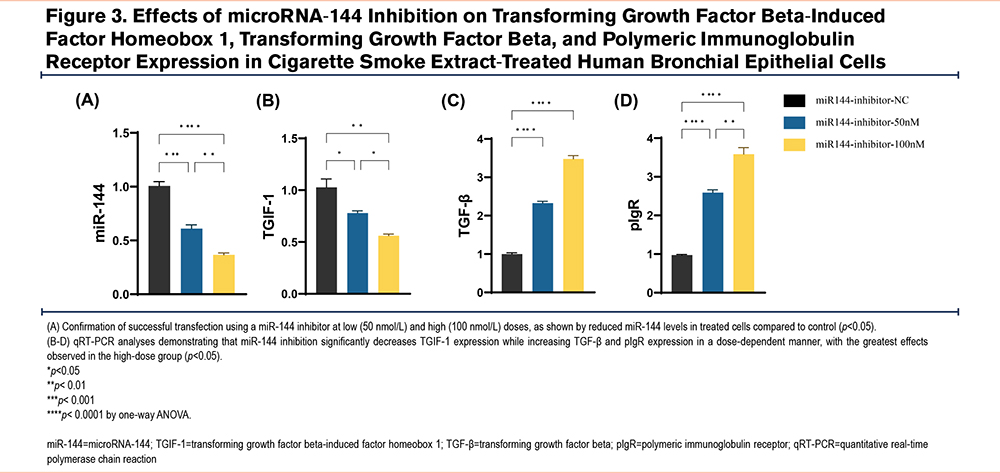
miR-144 Mediates Cigarette Smoke Extract-Induced Changes in TGIF-1, TGF-β, and pIgR Expression in 16HBECs
To investigate whether miR-144 is responsible for CSE-induced changes in TGIF-1, TGF-β, and pIgR expression, we used transient transfection to introduce a miR-144 inhibitor into mature, differentiated 16HBECs. The cells were divided into 3 groups: control, low-dose miR-144 inhibitor (50nmol/L), and high-dose miR-144 inhibitor (100nmol/L). Successful transfection was confirmed by qRT-PCR, showing reduced miR-144 levels in treated cells (Figure 3A). qRT-PCR analysis revealed that inhibiting miR-144 significantly decreased TGIF-1 expression, while TGF-β and pIgR levels increased in a dose-dependent manner, with the most pronounced effects in the high-dose group (Figure 3B-D).
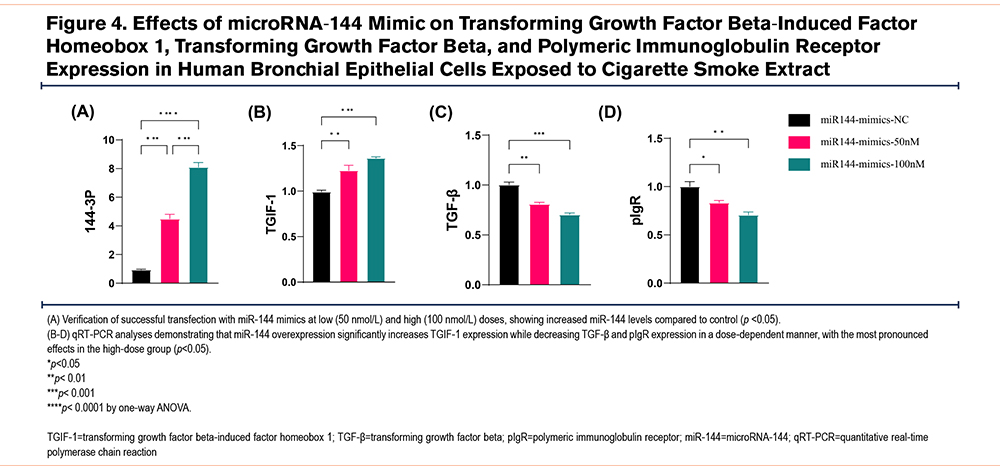
miR-144 Mediates Cigarette Smoke Extract-Induced Changes in TGIF-1, TGF-β, and pIgR Expression in 16HBECs
To further examine the role of miR-144, we introduced miR-144 mimics into mature and differentiated bronchial epithelial cells via transient transfection. Cells were divided into 3 groups: control, low-dose miR-144 mimic (50nmol/L), and high-dose miR-144 mimic (100nmol/L). Transfection success was verified by qRT-PCR, confirming increased miR-144 levels (Figure 4A). qRT-PCR analysis showed that mimicking miR-144 significantly elevated TGIF-1 expression, while TGF-β and pIgR levels decreased in a dose-dependent manner, with the strongest effects observed in the high-dose mimic group (Figure 4B-D).
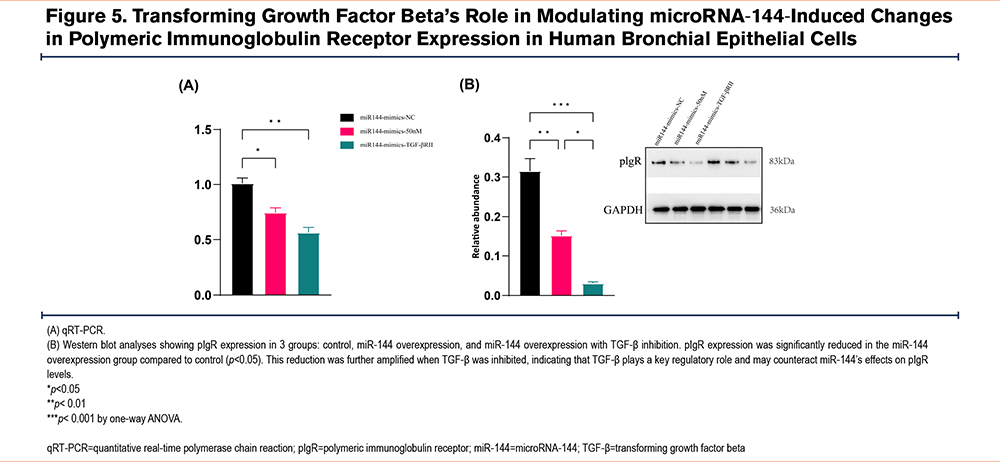
TGF-β’s Regulatory Role in miR-144-Induced pIgR Expression Changes
To validate TGF-β's role in regulating pIgR expression under miR-144 overexpression, we established 3 experimental groups: control, miR-144 overexpression, and miR-144 overexpression combined with TGF-β inhibition. qRT-PCR analysis revealed that pIgR expression significantly decreased in the miR-144 overexpression group compared to control. Notably, this reduction was further intensified with TGF-β inhibition, suggesting that TGF-β is crucial in regulating pIgR expression and may counteract the effects of miR-144 overexpression on pIgR levels (Figure 5A). Western blot analysis confirmed the protein expression changes of pIgR across those groups, consistent with the qRT-PCR results (Figure 5B).
Discussion
COPD is a progressive disorder characterized by persistent airway inflammation and remodeling, leading to impaired mucosal immunity and compromised airway function.1 Smoking and environmental pollutants are primary risk factors for COPD, often trigger AECOPDs by respiratory infections, further accelerate disease progression, and contribute to increased morbidity.1 In this study, we investigated the molecular mechanisms underlying airway immune barrier dysfunction in COPD, with a specific focus on the regulation of the pIgR and its secretory form, sIgA.21 In COPD patients, the pIgR-sIgA system is often disrupted, with notable downregulation of pIgR, especially in areas of epithelial hyperplasia or incomplete differentiation.21,22 This reduction in pIgR expression leads to lower sIgA levels, compromising mucosal immunity and increasing susceptibility to infections. These infections can lead to immune cell accumulation, such as macrophages and neutrophils, which drive chronic inflammation in the airways.21,22 A large cohort study identified a significant reduction in pIgR expression in the airway epithelium of patients with severe COPD compared to nonsmoking controls, non-COPD smokers, and individuals with mild COPD.23 Additionally, recent genome-wide association studies have reported decreased PIGR gene expression in airway intermediate and ciliated cells of non-COPD smokers.24 In COPD patients, pIgR downregulation is especially prominent in areas of bronchial epithelial remodeling, such as goblet cell hyperplasia, squamous metaplasia, and incomplete differentiation, that frequently exhibit sIgA deficiency.7 This deficiency weakens local mucosal immunity, increasing bacterial invasion and infiltration by immune cells, including macrophages and neutrophils. To model the chronic inflammatory environment of COPD, we exposed bronchial epithelial cells to CSE. CSE is a widely used in vitro model that replicates key aspects of chronic smoke-induced inflammation. Our study, therefore, focuses on the effects of CSE exposure, which involves distinct inflammatory triggers and regulatory mechanisms. Besides, prior research suggests that pIgR expression may be regulated by TGF-β signaling.23 In this study, we observed a marked decrease in pIgR expression in CSE-treated cells compared to controls and further examined CSE’s effect on the TGF-β signaling pathway. Results indicated a significant reduction in TGF-β levels and an increase in TGIF-1 expression after CSE treatment. As an upstream regulator, elevated TGIF-1 may contribute to TGF-β downregulation. Additionally, CSE treatment led to a notable upregulation of miR-144, supporting our hypothesis on its involvement in modulating the TGF-β pathway and influencing pIgR regulation.
Most importantly, recent research highlights significant roles of miRNAs in the pathophysiology of COPD.25 Among these, miR-144 has shown a strong association with COPD.25,26 Although evidence indicates that miR-144 may influence pIgR and sIgA, its precise regulatory mechanism remains unclear.25 In this study, we further investigated miR-144's role in a series of in vitro experiments. Our findings demonstrate that miR-144 overexpression significantly reduces pIgR expression, suggesting a potential role for miR-144 in compromising mucosal immunity in COPD. Furthermore, CSE exposure was associated with decreased TGF-β levels and increased TGIF-1 expression, indicating an alteration in the TGF-β signaling pathway, a critical regulator of pIgR expression. Notably, miR-144 appears to influence TGF-β signaling by modulating both TGF-β and TGIF-1 expression, thereby contributing to the observed reduction in pIgR levels. These findings provide mechanistic insights into how chronic smoke exposure may impair immune defense mechanisms in the airway epithelium. Interestingly, while miR-144 is generally expected to downregulate its target genes, we observed an increase in TGIF-1 expression following miR-144 overexpression and CSE treatment. This paradoxical finding suggests that additional regulatory mechanisms may be involved, potentially including compensatory transcriptional responses or feedback loops triggered by chronic inflammation. Future studies should further investigate the precise regulatory interactions between miR-144, TGIF-1, and TGF-β signaling in COPD pathogenesis.
It is important to acknowledge that while our study provides valuable insights into the chronic inflammatory phase of COPD, miRNA expression patterns and regulatory networks may differ significantly during acute exacerbations. Exacerbations involve heightened immune activation, pathogen-driven inflammation, and rapid shifts in epithelial responses, which may influence miR-144-mediated pathways in ways distinct from chronic exposure models. Future research should aim to elucidate the role of miR-144 in acute exacerbations and explore its potential as a therapeutic target in both chronic and acute phases of the disease.
In conclusion, our findings highlight a novel regulatory role of miR-144 in airway mucosal immunity, demonstrating its ability to modulate pIgR expression through the TGF-β signaling pathway in the context of chronic COPD inflammation. These insights provide a foundation for future studies examining miR-144 as a potential therapeutic target, with implications for restoring mucosal immunity and mitigating COPD progression.
Acknowledgments
Author contributions: HL was responsible for writing the original draft. HL, YZ, JC, and LL contributed to the methodology, formal analysis, and data curation. HL and JZ were responsible for the conceptualization. HL was responsible for the funding acquisition. JZ supervised and contributed to the investigation and the review and editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript submitted for publication
Data availability: Data are available upon request from the authors.
Declaration of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.